Prokaryotes are the simplest organisms. Eukaryotic cells are fundamentally different from those of.
 Evolution Into The Protista Modern Protista Represent The First Eukaryotes First Eukaryotes Evolved From Prokaryote Ancestors Modern Prokaryotes Represent Ppt Download
Evolution Into The Protista Modern Protista Represent The First Eukaryotes First Eukaryotes Evolved From Prokaryote Ancestors Modern Prokaryotes Represent Ppt Download
The eukaryotic ssDNA viruses apparently evolved via a fusion of genes from prokaryotic rolling circle-replicating plasmids and positive-strand RNA viruses.
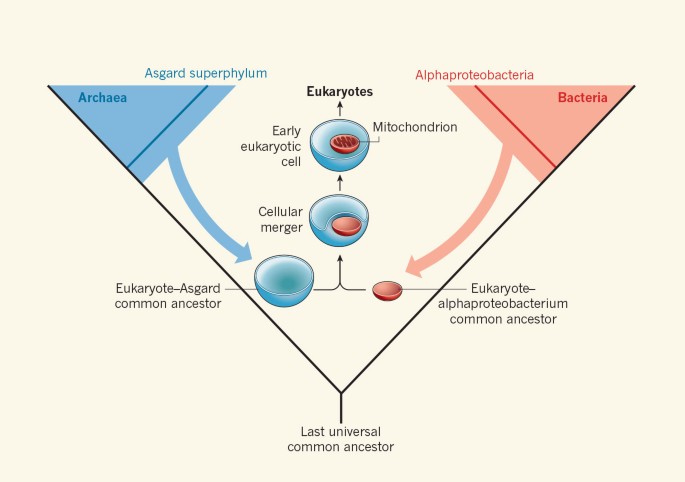
Evolution of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It was as if nature was experimenting to optimally utilize the gene pool without changing. As evolution progressed genetic alterations accumulated and a mechanism for gene selection developed. In both bacteria and archaea the vast majority of the viruses possess dsDNA genomes mostly within the range of 10 to 100 kb.
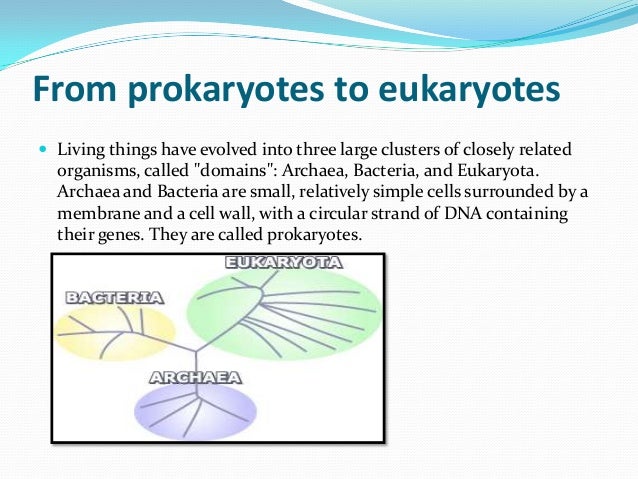
Archaea and Bacteria are small relatively simple cells surrounded by a membrane and a cell wall with a circular strand of DNA containing their genes. Cells are divided into two main classes initially defined by whether they contain a nucleus. Publisher Name Springer Boston MA.
Prokaryotes have at least ten times more biomass than eukaryotes. The second most common class includes small ssDNA viruses. This is particularly unfortunate given that it is arguably the most drastic evolutionary transition that has taken place since the emergence of the last universal common ancestor LUCA of all cellular life-forms.
For most biologists the big picture regarding the origin and evolution of prokaryotes and eukaryotes is not at issue and recent evidence only serves to back up the intuitively obvious. Eds Bacteria Bacteriophages and Fungi. A domain is the highest taxon just above the kingdom.
A distinct difference between prokaryotic chromosomes and eukaryotic chromosomes involves histones. There is a sharp divide in the organizational complexity of the cell between eukaryotes which have complex intracellular compartmentalization and even the most sophisticated prokaryotes archaea and bacteria which do not 46. From prokaryotes to eukaryotes Living things have evolved into three large clusters of closely related organisms called domains.
The eukaryotes developed at least 27 billion years ago following some 1 to 15 billion years of prokaryotic evolution. Prepared by group 5 2. Two proposed pathways describe the invasion of prokaryote cells by two smaller prokaryote cells.
The mitochondria-first hypothesis proposes mitochondria were first established in a prokaryotic host which subsequently acquired a nucleus to become the first eukaryotic cell. 1974 The Classification and Evolution of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. There are harmful prokaryotes but a majority are beign or helpful.
The evolution process includes genetic alterations that started with prokaryotes and now continues in humans. The third domain is Eukarya. The prokaryote domains are Bacteria and Archaea see Figure below.
Different families of eukaryotic dsDNA viruses appear to have originated from specific groups of bacteriophages on at least two independent occasions. Table 11 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Characteristic. Prokaryotes are found wherever there is life.
Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus. The first cells and organisms to evolve would be classified as prokaryotic. They are called prokaryotes.
Prokaryotes divide via using binary fission while eukaryotic cells divide via mitosis. They subsequently became successfully included as part of a now much larger cell with additional structures and capable of additional functions. Therefore a very early event in evolution appears to have been the.
The origin of eukaryotes is a major evolutionary transition for which we lack much information about intermediate stages. A distinct difference between prokaryotic chromosomes and eukaryotic chromosomes involves histones. Most single celled organisms have a cell wall around their plasma membranes in order to.
In the standard account prokaryotes predated eukaryotes by. The eukaryote-first hypothesis proposes prokaryotes actually evolved from eukaryotes by. Archaea Bacteria and Eukaryota.
Complex eukaryotes evolved from simpler prokaryotic ancestors. The viromes of prokaryotes and eukaryotes dramatically differ with respect to the contribution of the different Baltimore classes to the overall viral diversity. They can survive in a variety of weather conditions that eukaryotes cant survive in.
The Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells 01. The origin of eukaryotes is a huge enigma and a major challenge for evolutionary biology 13. Studies of their DNA sequences indicate that the archaebacteria and eubacteria are as different from each other as either is from present-day eukaryotes.
Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are either archaea or bacteria. Their cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. Positive-strand RNA and dsRNA viruses.
Evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 1. Prokaryotes are currently placed in two domains. Fossil records indicate that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes somewhere between 15 to 2 billion years ago.
Eukaryotes include larger more complex organisms such as plants and animals. ABSTRACTThe evolution process includes genetic alterations that started with prokaryotes and now continues in humans. As life on Earth started to undergo evolution and become more complex the simpler type of cell called a prokaryote.
 From Prokaryotes To Eukaryotes
From Prokaryotes To Eukaryotes
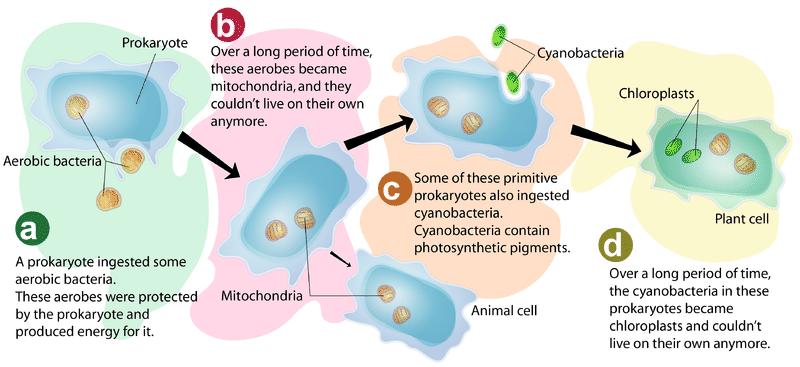
 Endosymbiosis The Origin Of Eukaryotic Cells
Endosymbiosis The Origin Of Eukaryotic Cells
 8 16d Endosymbiotic Theory And The Evolution Of Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts
8 16d Endosymbiotic Theory And The Evolution Of Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts
 Endosymbiosis And Eukaryotic Cell Evolution Current Biology
Endosymbiosis And Eukaryotic Cell Evolution Current Biology
 From Prokaryotes To Eukaryotes
From Prokaryotes To Eukaryotes
 Eukaryotes And Prokaryotes What Are The Similarities Differences And Examples
Eukaryotes And Prokaryotes What Are The Similarities Differences And Examples
 The Rise Of Photosynthetic Eukaryotes A During An Evolutionary Download Scientific Diagram
The Rise Of Photosynthetic Eukaryotes A During An Evolutionary Download Scientific Diagram
-
Chapter Two CLASSIFICATION OF PENALTIES Art. The Debate Over Death Penalty. Death Penalties Around The World Three widely used execution ...
-
MacArthur arrived at his post a World War II hero having successfully led multiple troops through the war. Douglas MacArthur Is One of Ameri...
-
10 Reasons Not To Become An Archaeologist (and Why. . 5. Being Sent Indoors. Promotion comes slowly to archaeologists, and when it doe...
disadvantages of being an archaeologist
10 Reasons Not To Become An Archaeologist (and Why. . 5. Being Sent Indoors. Promotion comes slowly to archaeologists, and when it doe...

ads